Usage-Based vs Flat Rate Pricing
Key differences between usage-based and flat-rate pricing models for SaaS businesses, including benefits, challenges, and customer preferences.
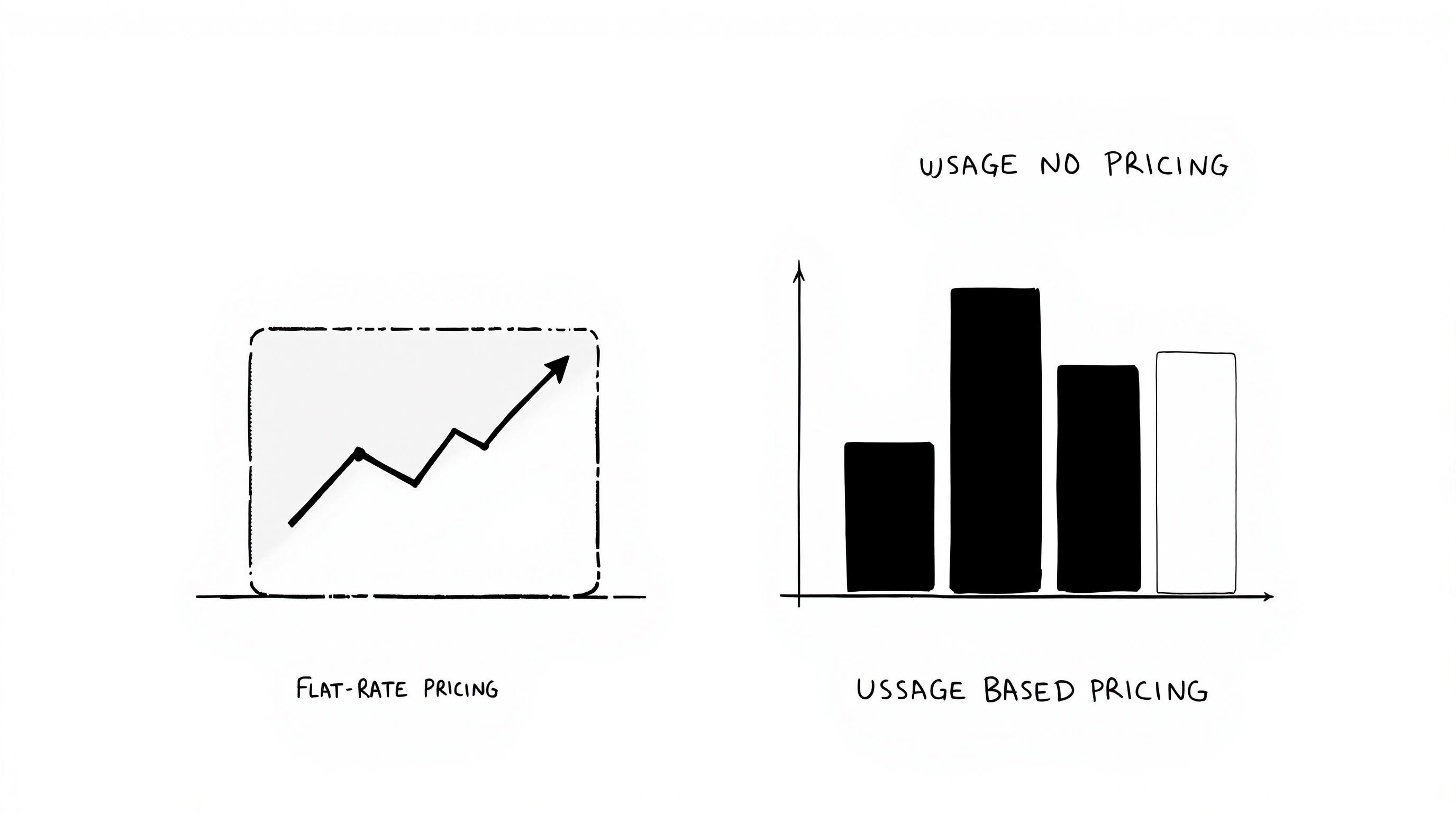
Choosing the right SaaS pricing model can impact your revenue and customer satisfaction. Here’s a quick breakdown of the two main approaches:
- Usage-Based Pricing: Customers pay based on how much they use. Great for flexibility but may lead to unpredictable revenue.
- Flat-Rate Pricing: A fixed monthly fee for consistent costs. Easy to understand but less adaptable to varying usage.
Quick Comparison
| Factor | Usage-Based | Flat-Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Varies with usage | Fixed monthly fee |
| Revenue | Fluctuates with customer use | Predictable and stable |
| Customer Appeal | Transparent, scalable | Simple, easy to budget |
| Scalability | Grows with usage | Requires manual upgrades |
| Best For | Variable usage patterns | Steady, predictable usage |
Both models have pros and cons. Usage-based pricing suits fluctuating needs, while flat-rate pricing works for consistent use. Some businesses may even combine the two for flexibility.
Flat vs. Usage Pricing: The Best Model for Early SaaS?
Core Elements of Both Pricing Models
Let’s break down how usage-based and flat-rate pricing actually work. Understanding these elements can help SaaS businesses decide which approach fits their product and audience.
How Usage-Based Pricing Works
This model charges customers based on how much they use a service. To make it work, you need systems that can monitor and bill for usage accurately:
- Usage Metrics: Tracks actions like API calls, data storage, or user activity.
- Billing Cycles: Keeps tabs on usage over specific time periods.
- Rate Structure: Includes tiered pricing or discounts for higher usage levels.
For example, a company might charge per API call, with costs scaling as the customer uses more.
How Flat-Rate Pricing Works
Flat-rate pricing keeps things simple: one fixed fee for access to a set of features. This approach is predictable and easy to understand:
- Fixed Fee: A consistent monthly or annual charge.
- Feature Sets: Includes a predefined bundle of tools and capabilities.
- Service Limits: Clearly outlines any usage caps or restrictions.
Customers pay one price for full access to the service.
Main Differences Between Models
These two pricing models differ in how they handle costs, revenue, and customer expectations. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Aspect | Usage-Based | Flat-Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Billing Complexity | Costs vary based on actual usage | Fixed fee, regardless of usage |
| Revenue Predictability | Changes with customer usage patterns | Stable and consistent |
| Customer Commitment | Lower initial commitment | Requires upfront payment |
| Scalability | Costs grow with usage | May need manual plan upgrades |
| Implementation | Needs advanced tracking tools | Managed with simple subscription systems |
These differences highlight when each model works best. Usage-based pricing is ideal for services where demand fluctuates, while flat-rate pricing is better for products with steady usage and clear feature bundles.
For SaaS companies, SaaS boilerplates can simplify billing - whether you need to track usage or manage flat-rate subscriptions. The right choice depends on your product and audience. Usage-based pricing thrives with flexible consumption, while flat-rate pricing suits products with consistent, predictable use.
Benefits and Drawbacks
Usage-Based Pricing: Pros and Cons
Usage-based pricing has its upsides and challenges. This approach works best when customer usage varies significantly.
Advantages:
- Costs align directly with the value customers receive
- Low upfront cost encourages early adoption
- Revenue grows as customer usage increases
- Offers detailed usage data to refine the product
Challenges:
- Requires a complex billing system
- Monthly revenue can be unpredictable
- Customers may need clear guidance on usage
- Sales processes can become more complicated
- Higher customer support expenses
These points highlight the trade-offs involved when adopting this pricing model.
Flat-Rate Pricing: Pros and Cons
Flat-rate pricing is popular for its simplicity and predictability.
Advantages:
- Provides stable and predictable revenue
- Easy for customers to understand
- Reduces operational complexity
- Simplifies budgeting for customers
Challenges:
- Misses out on additional revenue from heavy users
- Risk of losing customers if perceived value doesn’t match cost
- Limited flexibility for diverse customer needs
- May feel costly for smaller customers
- Harder to monetize growing customer usage
These pros and cons provide a clear basis for comparing the two pricing models.
Side-by-Side Model Comparison
Here’s a quick comparison of how these models stack up on key business factors:
| Factor | Usage-Based | Flat-Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue Predictability | Variable month-to-month | Highly predictable |
| Ease of Customer Acquisition | Easier (low upfront cost) | Harder (requires commitment) |
| Scalability | Grows automatically with usage | Requires plan upgrades |
| Value Capture | Matches usage | Fixed, regardless of usage |
| Cash Flow | Variable but can grow higher | Stable but potentially lower |
| Customer Satisfaction | Better for varied usage | Better for consistent usage |
This table highlights the trade-offs between the two models, especially in terms of revenue and customer experience.
The right choice depends on your SaaS product, target audience, and goals. Usage-based pricing is ideal for services like APIs or infrastructure where usage varies widely. Flat-rate pricing works better for products with steady usage and clearly defined features.
Best SaaS Boilerplates offers starter kits that support both pricing structures, making it easier to implement whichever strategy fits your business.
Effects on SaaS Business Performance
The pricing model you choose directly affects revenue patterns, customer behavior, and operational needs, which all play a role in shaping your business outcomes.
Revenue Stability vs Growth
Flat-rate pricing ensures steady monthly recurring revenue (MRR), making financial planning and investor communications simpler. On the other hand, usage-based pricing allows revenue to grow alongside customer usage, though it introduces variability in cash flow.
| Revenue Aspect | Usage-Based | Flat-Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Predictability | Changes month-to-month | Consistently stable |
| Growth Pattern | Scales with usage | Grows through plan upgrades |
| Revenue Ceiling | No cap with usage | Limited by pricing tiers |
| Cash Flow | Can fluctuate | Steady and reliable |
| Forecasting Accuracy | Less precise | Highly accurate |
These differences in revenue patterns also influence how you attract and retain customers.
Customer Growth and Loyalty
Usage-based pricing lowers the barrier for new users, making it easier to attract customers. Flat-rate pricing, with its predictable costs, tends to build loyalty among organizations that rely on consistent pricing.
Business Operations and Growth
The operational needs of each pricing model also impact how your business runs. Usage-based pricing requires tools for real-time usage tracking, advanced billing systems, and detailed analytics. Flat-rate pricing, on the other hand, simplifies operations, allowing your team to focus more on sales and marketing. These streamlined processes help maintain revenue stability and strengthen customer retention.
Customer Response to Pricing
Customer Experience with Usage-Based Plans
Usage-based pricing works well for startups and SMBs by charging only for what they use. This approach eliminates the stress of committing to a fixed monthly fee, especially when usage can be unpredictable. With clear tracking tools, customers can keep tabs on their costs in real time.
| Customer Segment | Key Benefits | Common Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| Startups | Lower upfront costs, scalability | Usage unpredictability |
| SMBs | Flexible budgeting, better cost control | Fluctuating monthly bills |
| Enterprises | Optimized resources, ROI tracking | Challenges in budget forecasting |
Customer Experience with Flat-Rate Plans
For organizations with steady usage, flat-rate plans are the go-to option. This model simplifies resource planning by removing the need to constantly monitor usage metrics. These contrasting experiences highlight the factors that shape customer preferences.
What Drives Customer Choice
Customer feedback underlines the distinct factors that influence decisions between usage-based and flat-rate pricing models. Here’s what typically affects their choice:
- Budget Predictability: Companies with fixed budgets lean toward flat-rate plans for stable costs.
- Variable Usage: Businesses with fluctuating needs often find usage-based pricing more practical.
- Growth Stage: Early-stage companies tend to pick usage-based models for their flexibility.
Business maturity plays a big role. Startups and younger businesses often choose usage-based pricing to keep initial costs low. On the other hand, established companies prefer flat-rate plans for the consistency they offer. For businesses with seasonal demand, usage-based pricing is especially appealing, as it lets them adjust costs with their activity levels rather than paying for a higher-tier plan year-round.
Selecting Your SaaS Pricing Model
Once you’ve analyzed revenue and customer impacts, the next step is to align these insights with your business strategy by choosing the right pricing model.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Pricing Model
Your pricing model should reflect your product’s usage patterns, customer needs, and operational setup. Here’s a quick comparison to help you decide:
| Factor | Best for Usage-Based Pricing | Best for Flat-Rate Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Usage Pattern | High variability in consumption | Consistent, predictable usage |
| Customer Base | Diverse needs and scales | Similar usage across customers |
| Technical Infrastructure | Strong usage tracking systems | Basic feature tracking |
| Market Position | Competitive, growth-oriented | Established and stable |
| Resource Costs | Costs tied to usage levels | Fixed operating costs |
When to Choose Each Model
Usage-based pricing is ideal when customer value depends on how much they use your service. Think cloud storage or data processing platforms, where user needs can vary greatly.
Flat-rate pricing works well when:
- Customer usage is steady and predictable
- Service delivery costs don’t fluctuate
- Customers prefer predictable billing
- Your product includes all key features in a single package
Combining Pricing Models
A hybrid pricing strategy can blend the benefits of both models while minimizing their downsides. For instance, you could:
- Charge a base subscription fee with optional usage-based add-ons
- Use tiered pricing, where each tier has a flat rate
- Offer core features at a flat rate and premium features on a usage basis
The key is to keep mixed pricing simple and easy to understand, so customers know what to expect while still enjoying flexibility.
For SaaS businesses ready to dive into these pricing models, a good SaaS starter kit can help you build billing systems that handle even complex pricing structures with ease.
Conclusion: Making Your Decision
Key Takeaways
Deciding between usage-based and flat-rate pricing means looking closely at your SaaS’s usage patterns, technical setup, growth plans, and market positioning. Here’s a quick recap of the main factors discussed:
- Usage Patterns: Understand how customers use your service and their behavior.
- Technical Setup: Ensure your infrastructure can handle accurate usage tracking and billing.
- Growth Goals: Match your pricing model to your revenue and expansion plans.
- Market Fit: Factor in your competition and the needs of your target audience.
With these points in mind, you can create a pricing strategy that fits your business while keeping customers in mind. A mix of both pricing methods can also work to meet your goals.
Best SaaS Boilerplates for SaaS Development
When you’re ready to implement, Best SaaS Boilerplates offers starter kits with built-in billing systems for any pricing model. These include:
- Authentication systems
- Subscription management tools
- Usage tracking features
- Billing integration
This setup allows you to focus on perfecting your pricing strategy while relying on a strong billing system. Whether you go for usage-based, flat-rate, or a hybrid model, these tools help ensure your approach is effective and scalable.
Recommended SaaS Boilerplates
Below you’ll find three highly nominated SaaS boilerplates that reliably support usaged-based and/or flat-rate pricing models.